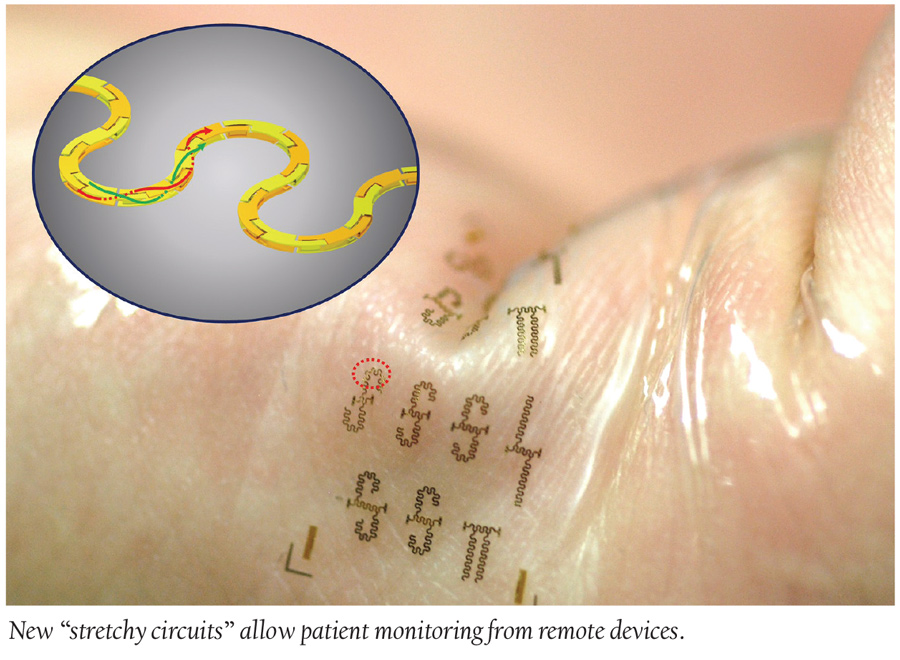
Medical Devices: Stretchy Circuits to Change the Wearables World
Newly developed stretchy circuits are about to revolutionize the growing wearables market. Zhenqiang “Jack” Ma leads a team of scientists from the University of Wisconsin who just developed the world’s fastest, stretchable integrated circuits. These highly efficient twists of segmented metal blocks not only allow for comfort in body adhesives and clothing, but can also introduce biomedical wearables to the 5G realm where vitals can be recorded and transmitted remotely and wirelessly for all sorts of convenient medical usages. With this breakthrough, healthcare staff can have constant access to patient monitors from remote devices, and patients can be more comfortable without invasive instruments and wires.
Doctor Docs: Millennial Doctors Change the Healthcare Dynamic
A national survey has revealed that millennial physicians, defined as general practitioners between 26 and 36 years old, change their relationship with patients based on age. Millennial doctors want a more collaborative treatment approach with patients close to their age, to encourage them to do research on their own and have conversations with peers about treatment options. They’d even like pharma companies to get involved with patient healthcare by offering discussion guides and adherence support.
As a result, most millennial physicians think peers are the biggest influence on patients and according to GSW, PALIO, and inVentiv Health study, only 16% find pharma promotion to be influential. Eighty-one percent think pharma’s DTC advertising makes their job more difficult because patients ask for medications they don’t need and won’t receive from this new generation of doctors. Instead, these docs are shaping healthcare to match their peers’ unique needs.
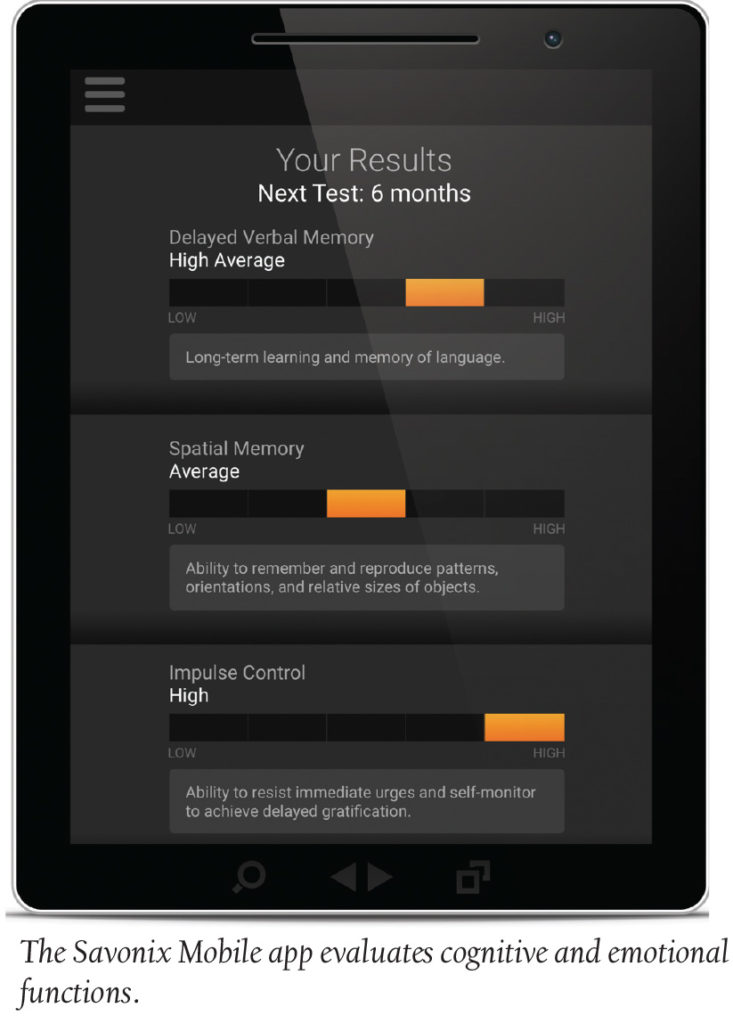
TeleMed Text: Neuroscientific Testing—There’s an App for That
Savonix has revolutionized access to brain data by launching the beta version of Savonix Mobile, an app that serves as the most accurate professional tool for evaluating cognitive and emotional functions. Following a closed beta session with a selection of industry leaders, the public will have access to the app for the next few weeks in order to leave user feedback for the only mobile, digital cognitive assessment app on the market. The 30-minute assessment is suitable for children and adults and can test anything from verbal memory to emotion regulation.
Former Stanford Medical healthcare professionals, who used decades of data from clinical trials in cognitive assessment, built Savonix Mobile. “We are unleashing the power of neurocognitive assessment by making it affordable and widely accessible, all in the palm your hand,” Savonix founder Mylea Charvat, PhD said in a statement. During the open beta time, users will receive results on their mobile app, which can be presented to clinicians.
Research & Development: Space Research Could Help us Design Pills
The Hard to Wet Surfaces research taking place in the International Space Station is helping researchers understand how pharmaceuticals dissolve in liquid-solid interactions, which could be a big help in designing medicine tablets that work faster. Scientists will test wettability and float effect, crucial variables in liquid-solid interactions, in microgravity. These results will reveal data about wettability that happens too rapidly during dissolution on Earth to understand, which can then direct pharma companies in choosing faster dissolving ingredients.
“We hypothesize that tablets that float on Earth will dissolve more quickly in microgravity because they will not float in space. More of the surface will be in contact with the liquid,” said Alison Campbell, a Senior Research Scientist at Eli Lilly & Company, in a statement. Furthermore, studies in microgravity may reveal that some medications are less effective when taken in space, a phenomenon that is important to our current astronauts and future space travelers.
Discoveries/Innovations: Origami DNA Opens a Door to New Opportunity
Only a small group of experts in the field of DNA origami were able to build 3D replicas on a nanometer scale until researchers at MIT built an algorithm to do months of work instantaneously. Project leader Mark Bathe, PhD said in a statement, “Our hope is that this automation significantly broadens participation of others in the use of this powerful molecular design paradigm.” The algorithm, DAEDALUS, can build any 3D shape without manual intervention. The origami DNA could provide a scaffold for viral peptides and proteins for use as vaccines. The nanoparticle structure can be designed with any combination of peptides, which could mimic a virus that appears in our bodies, or countless other structures that could have a huge impact on biomedical research.
FDA Update
Drug Approvals
Promius Pharma, the U.S. subsidiary of Dr. Reddy’s, has received FDA approval of Sernivo, a prescription topical steroid for treatment of mild to moderate plaque psoriasis. Treatment success with the steroid spray has allowed for the commercial launch in the coming quarter with promises for further medical dermatology products in the U.S. market for the future.
Gilead received FDA approval of Epclusa, the first oral, single-tablet regimen for adults with genotype 1-6 chronic Hepatitis C virus infection. The drug has the potential to eliminate HCV-infected patients, regardless of genotype.
The first generic for Tamiflu, Roche’s oseltamivir phosphate, is indicated for treatment of Influenza A and B in patients ages two weeks and older, who have flu symptoms for less than 48 hours, and for flu prevention in patients one year old and above.
Galderma received FDA approval for Differin gel, the first OTC retinoid for the treatment of acne. The gel is applied daily and includes the first new active ingredient in an OTC drug for acne treatment since the 1980s.
The FDA granted priority review for Nicox’s AC-170, an eye drop for ocular itching associated with allergic conjunctivitis. The FDA has a goal date of October 18, 2016 for the new eye drop formulation.
Med Device Approvals
Gore received FDA approval for the GORE TIGRIS self-expanding stent for peripheral artery disease. The device is designed to improve anatomical conformability with natural knee movement when treating Peripheral Artery Disease.