Doctor Docs: Medical Apps Fail Physicians in China
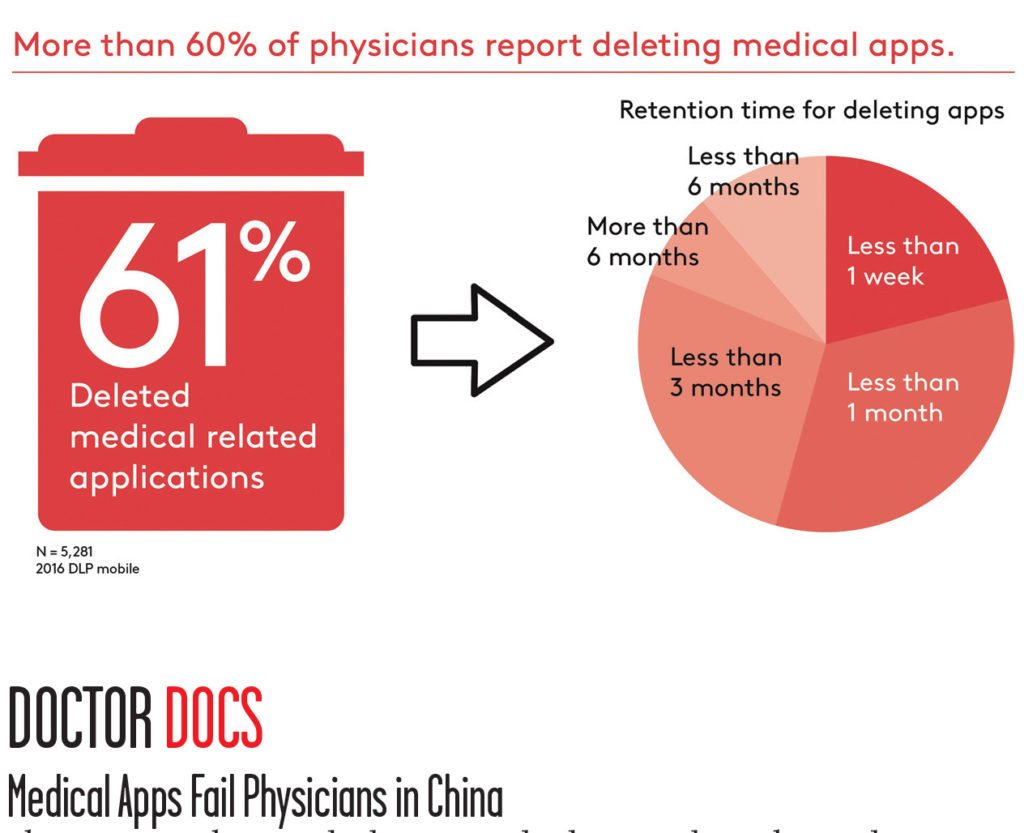 Physicians in China are looking at medical apps to keep their industry knowledge up to date. Kantar Health’s recent survey of more than 10,000 doctors reveals that doctors spend at least 10 hours a week doing online activities related to their profession and 90% are subscribing to medical apps for information they need. However, within a month, about 60% of doctors delete their apps, finding them not useful. This indicates app makers need to provide more relevant information, useful tools, and keep their knowledge base as up to date as possible. If more updated and relevant medical web knowledge is made available to doctors, it can have a profound effect on patient care.
Physicians in China are looking at medical apps to keep their industry knowledge up to date. Kantar Health’s recent survey of more than 10,000 doctors reveals that doctors spend at least 10 hours a week doing online activities related to their profession and 90% are subscribing to medical apps for information they need. However, within a month, about 60% of doctors delete their apps, finding them not useful. This indicates app makers need to provide more relevant information, useful tools, and keep their knowledge base as up to date as possible. If more updated and relevant medical web knowledge is made available to doctors, it can have a profound effect on patient care.
TeleMed Texts: New Tech Simulates Brain Damage
A certain amount of guesswork goes into the extremely important decisions surgeons make when performing a craniectomy, a procedure that consists of cutting a hole in the skull to relieve the pressure of a swelling brain. After brain trauma, the billions of axons that comprise the brain swell, causing a pressure in the cranium that can be life threatening. Because no tissue samples can be taken from the brain, surgeons rely on experience when creating a hole through the cranium to ensure that the axons don’t stretch too far to stop misshaping of the brain while allowing enough space to relieve pressure.
A group of researchers in Stanford is now developing a computer simulation of the brain that provides a color-coded map of damage after trauma. The simulation shows axonal stretching in a range of severity shown in red to green to blue. The technology can then display the effects on the brain after simulating a hole in a certain place and diameter in the cranium. This will allow surgeons to visualize the damage before surgery and make much more informed decisions about where and how big to make the opening in the skull.
Discoveries/Innovations: New Brain Imagery Technique Helps With Alzheimer’s
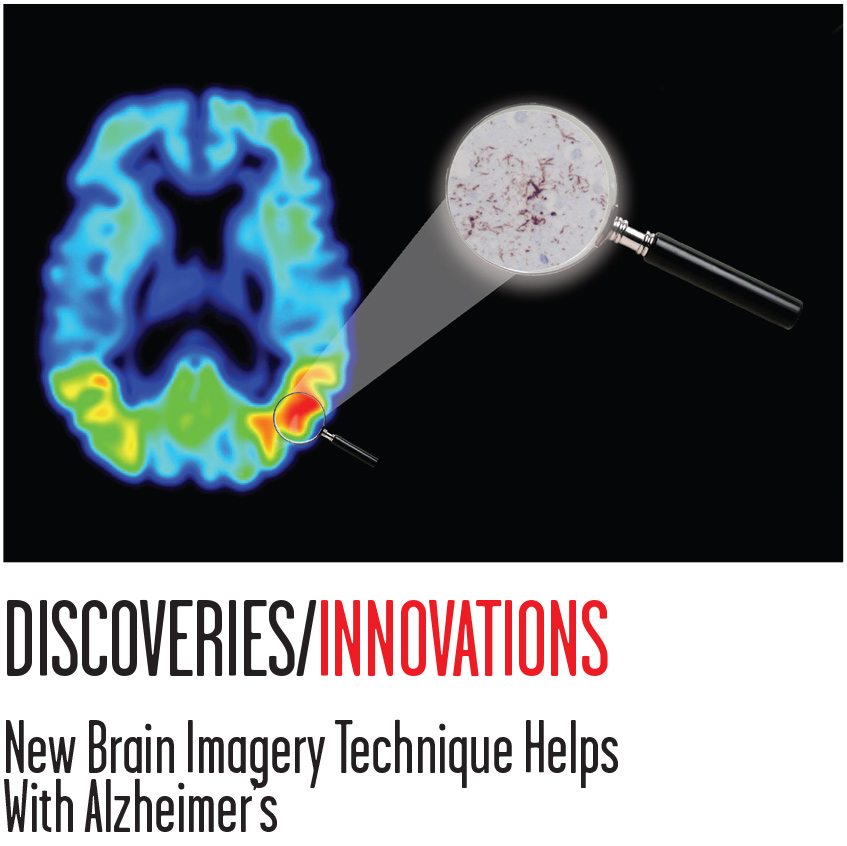 Many institutions are now using the Tau PET imaging technique to take brain scans of patients with Alzheimer’s. This works by revealing the protein called “tau” in the brain, which accumulate in those with Alzheimer’s and lead to brain cell death. This method has recently been proven by scientists at Lund University, Sweden to work extremely well. The Lund researchers proved this by comparing brain tissues of a deceased patient with his recent tau PET scan.
Many institutions are now using the Tau PET imaging technique to take brain scans of patients with Alzheimer’s. This works by revealing the protein called “tau” in the brain, which accumulate in those with Alzheimer’s and lead to brain cell death. This method has recently been proven by scientists at Lund University, Sweden to work extremely well. The Lund researchers proved this by comparing brain tissues of a deceased patient with his recent tau PET scan.
Ruben Smith, researcher at Lund University and physician at Skåne University Hospital says, “There are new candidate drugs that aim to reduce the accumulation of tau. The imaging method opens up opportunities to investigate the development of the disease at a detailed level, and to observe how tau aggregates are affected by the drugs.” The reliable reproduction of tau protein in the brain can help researchers track its accumulation over time and test new diagnostics and develop new therapies.
Medical Devices: Medtronic Releases Artificial Pancreas
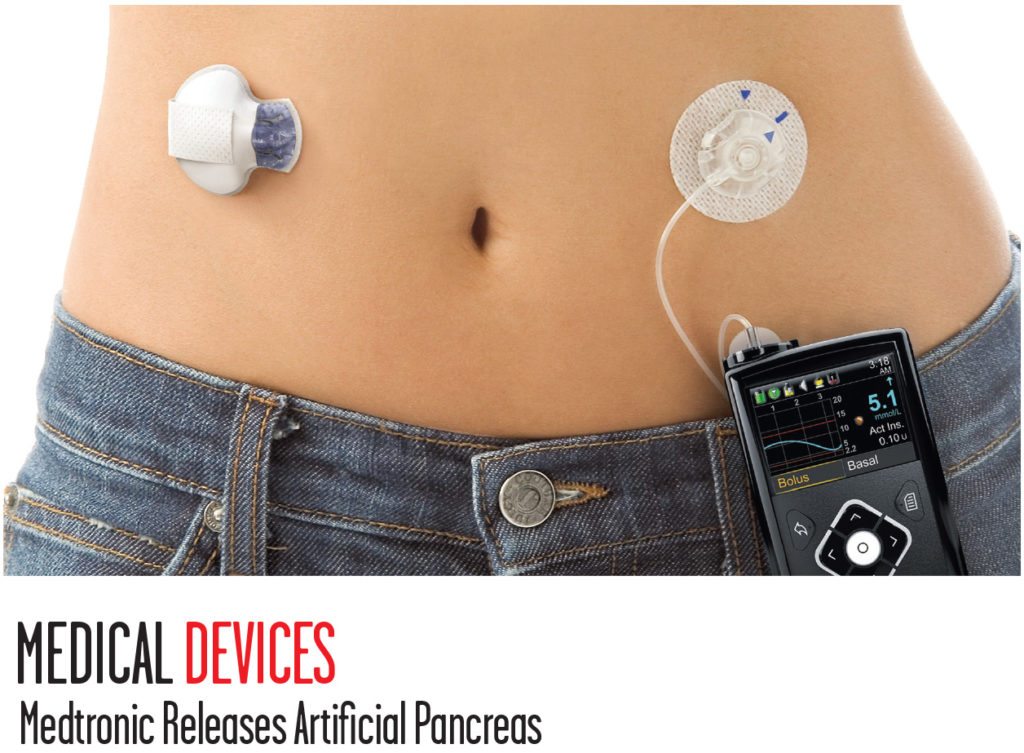 Medtronic now provides a new device that acts as an artificial pancreas for patients with type 1 diabetes. The MiniMed 670G monitors glucose levels in the wearer every five minutes and automatically administers insulin when needed. The MiniMed 670G consists of a sensor under the skin and an insulin pump strapped to the body with an attached catheter. This is the first medical device that can administer insulin automatically. The technology aims to give type 1 diabetes patients more freedom from the constant worry of checking glucose levels and injecting themselves.
Medtronic now provides a new device that acts as an artificial pancreas for patients with type 1 diabetes. The MiniMed 670G monitors glucose levels in the wearer every five minutes and automatically administers insulin when needed. The MiniMed 670G consists of a sensor under the skin and an insulin pump strapped to the body with an attached catheter. This is the first medical device that can administer insulin automatically. The technology aims to give type 1 diabetes patients more freedom from the constant worry of checking glucose levels and injecting themselves.
Therapeutic Talk: Children Pave the Way for New HIV Therapies
We now know that 5% to 10% of children infected with HIV show no disease progression, a control that only 0.3% of infected adults share. An Oxford University study claims that this could open a new horizon for HIV treatment for adults and children alike. While the 0.3% of adults owe their HIV control to the HLA class I molecules, children’s immune systems seem to guard themselves by not overreacting to the virus. By studying this newly discovered mechanism, scientists may be able to develop more effective therapies to cease the progression of HIV in adults.
Trend Setting: New Nanotech “Fish” Offer a Number of Medical Uses
Active transport via nanotechnology is an area of research for medicine delivery, non-invasive surgery, and single cell manipulation. Jinxing Li at the University of California made a breakthrough in nanotechnology, creating metal devices that swim like a fish and are 100 times smaller than a grain of sand. The head and tail of the fish, made of gold segments, oscillate when exposed to an electromagnetic field and propels it forward—like a fish. Justin Gooding of the University of New South Wales, Australia, says, “Active transport has recently begun to be explored and this work shows that active transport particles can be made smaller and faster.” This makes them perfect candidates for the next minimally invasive drug therapies.
FDA Update
Drug Approvals
Merck’s Zinplava has been approved to reduce recurrence of Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) for patients 18 years old and up who are receiving antibacterial drug treatment of CDI and are at high risk for recurrence. The medication does not treat CDI, and should only be used in antibacterial treatment of CDI.
The FDA has approved a Larken Laboratories, Inc.’s generic combination drug containing acetaminophen, caffeine, and dihydrocodeine bitartrate. The tablet is used for mild pain relief. Dihydrocodeine is an opioid pain medication whose effects are increased by acetaminophen, while caffeine stimulates the central nervous system to promote blood flow. Indicated for adult pain relief, tablets will be available in 325mg, 30mg, and 16mg.
Endo Pharmaceuticals received supplemental approval for Belbuca, a prescription drug for chronic pain. Belbuca is a patch worn by patients that releases long-term release opioids. It is used only for around-the-clock pain as it is more convenient and safer than using immediate release opioids throughout the day for constant pain.
Orphan Drug Designation
Yisheng Biopharma Co. received orphan drug designation for YS-ON-001, indicated for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma, and anti-tumors efficacy against breast, lung, liver, and other cancers in animals, who experienced no significant safety concerns compared to first-line chemotherapies or targeted therapies in animal studies. The drug is entering clinical development in multiple countries.
Med Device Approvals
Carl Zeiss Meditec Inc.’s VisuMax Femtosecond Laser, a tool designed for use in small incision lenticule extraction for adults with nearsightedness received FDA approval. The laser is used to remove tissue from the eye to permanently reshape the cornea to correct nearsightedness. It is indicated for those 22 years and older.





