During the last 100 years since the discovery of insulin, a hormone that helps the body regulate blood glucose levels, the repertoire of tools available to the healthcare community for diabetes has exploded. Today, patients have multiple ways to manage their glucose levels with a wide range of diabetes management devices. Alira Health’s report “Diabetes Management Devices: Market Trends 2023”1 analyzes the market landscape, examines the trends, and highlights some of the common challenges faced by players.
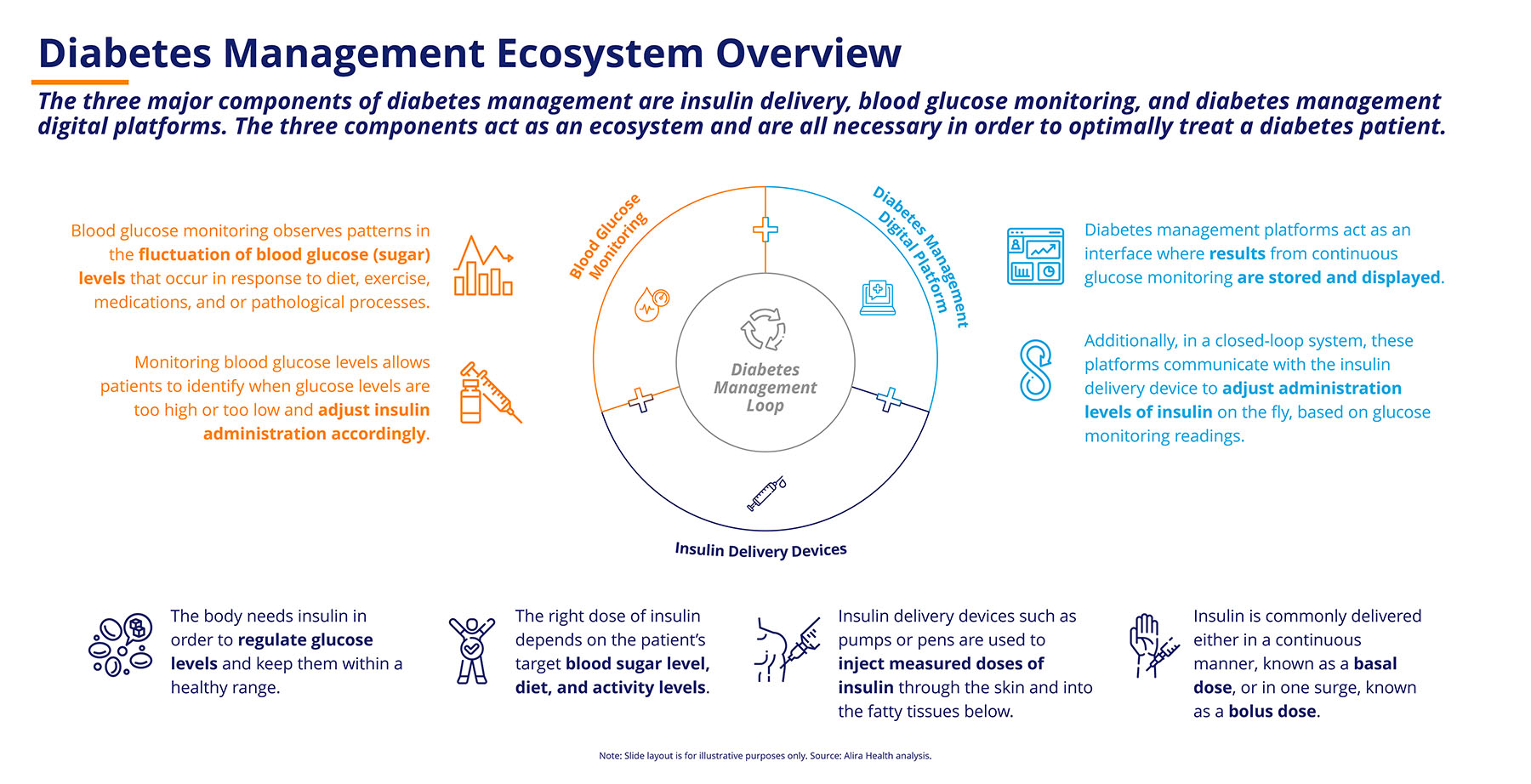
The Diabetes Management Ecosystem
Diabetes management devices fall into three segments:
1. Insulin delivery devices. These include insulin pens, syringes and, most recently, pumps that deliver insulin continuously. The classic delivery devices, pens and syringes, today often feature digital enhancements that enable patients to control and track how much insulin is delivered. However, patients and physicians are still faced with two critical questions: what is the right amount of insulin to inject and when is the right time to inject it? The other two product segments help address these questions.
2. Blood glucose monitoring devices. Patients need to know their current and expected glucose levels to determine how much insulin must be administered throughout the day. These devices fall into two major subsegments:
- Traditional blood monitoring glucose (BMG) devices and strips that allow the patient to measure glucose at a particular point in time. These systems demand manual intervention, interpretation, and commitment from patients to be effective tools.
- Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices are biosensors that continuously or intermittently measure the glucose levels from the blood. They are worn on the surface of the body and require minimal manual intervention.
Many patients find it difficult to translate the glucose levels reported by these devices to the required quantity of insulin. This is a critical decision because both higher and lower levels of insulin can be harmful to the patient. This leads us to the third segment of diabetes medical devices.
3. Digital management platforms. These devices bridge the glucose monitoring and insulin delivery devices by consolidating data from both systems. Digital platforms provide insights to patients and physicians about the trends in glucose levels and insulin doses consumed and help inform the appropriate quantities and timings of insulin doses to reverse identified trends.
These three segments of medical devices come together in different ways to improve patients’ experience in managing their disease (Figure 1). In traditional open-loop systems, the physician or patient must interpret the data that is collected by the digital platforms or from data logs and then decide on an insulin dosage regimen. Recently, more advanced closed-loop systems (also known as an artificial pancreas) include integrated continuous glucose monitoring systems, insulin delivery systems, and the required digital management platforms to significantly reduce the amount of manual intervention required to manage glucose levels.
 Regulatory & Market Access Challenges
Regulatory & Market Access Challenges
Today, diabetes management device manufacturers face multiple regulatory and market access challenges. The report dives into three key challenges:
- Transition to Medical Device Regulation (MDR). For manufacturers that aim to commercialize their products in the EU, the transition from the Medical Device Directive (MDD) to the new MDR regulatory framework is expected to introduce significant complexities. Companies will need to gather comprehensive clinical data and change their technical documentation and quality management systems.
- Post-market surveillance requirements (PMS). The MDR framework requires manufacturers to have a PMS program. Likewise, the FDA now has the authority to require manufacturers to conduct post-market surveillance at the time of approval or at any time later. Companies will need to establish and implement these programs in both regions in order to secure and maintain approval status.
- Price pressure on new technologies. Payers everywhere seek efficiency. In the EU, budget constraints are significant, and in the U.S., the focus is shifting to value-based care. Manufacturers are under pressure to justify their price goals and must present evidence of both the clinical and economic value of their solutions.
Key Trends in Regulatory & Market Access
Diabetes device manufacturers need to be aware of key trends affecting both regulatory approvals and market access today that are increasing the pressure on manufacturers to comply with changing requirements and generate more evidence and documentation than ever.
The first two trends are driven by the MDR challenge. MDR exacerbates an existing bottleneck in device approvals globally. As many as 500,000 products need to be reviewed for MDR compliance. The second trend is manufacturers are pivoting to prioritize FDA approval because MDR compliance is much more stringent than MDD.
Another big trend in medical devices is the development of regulatory pathways for digital health solutions. In the EU, Germany is the first country to create a dedicated framework for reimbursement of digital solutions, and in the U.S., the FDA ran a pilot program to pre-certify digital health software. The movement in both regions is towards a structured process for approval, so manufacturers must be aware of these evolving requirements and develop plans to address them. Companies that are prepared will gain a competitive advantage.
The final noteworthy trend is a shift to value-based care models and agreements. Payers in the U.S. and increasingly in the EU want manufacturers to provide data linking price and reimbursement for a medical device with the economic value of the health outcomes that it generates.
Diabetes Devices Market Outlook
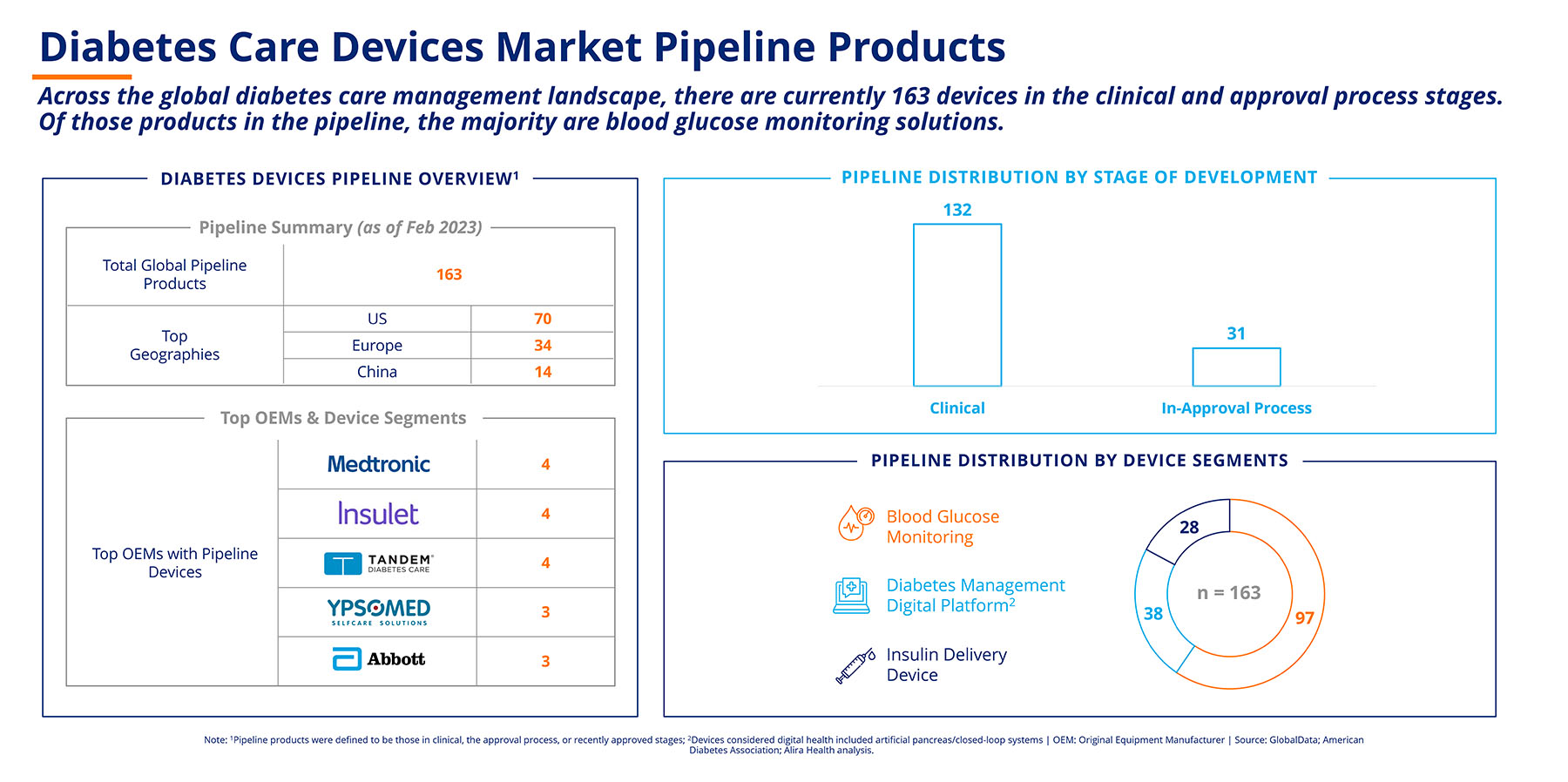
The outlook in the diabetes devices market is extremely positive. Currently, as cited in the report, 163 devices are in the clinical and approval process stages across the global diabetes care management landscape (Figure 2). Most of these devices are blood glucose monitoring solutions. These products will be affected by the regulatory and market access challenges and trends discussed above.
 The market is driven by two major factors. The first is the prevalence of diabetes, which is expected to grow at close to 4% Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR), resulting in more patients than ever requiring solutions. The other factor of market growth is that the additional value brought by innovative devices will mean that manufacturers can demand higher prices. As a result, the total market size is expected to increase rapidly.
The market is driven by two major factors. The first is the prevalence of diabetes, which is expected to grow at close to 4% Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR), resulting in more patients than ever requiring solutions. The other factor of market growth is that the additional value brought by innovative devices will mean that manufacturers can demand higher prices. As a result, the total market size is expected to increase rapidly.
Reference:
1. https://alirahealth.com/education-hub/diabetes-market-trends-2023.