The COVID-19 pandemic uncovered even more proof of just how important it is to address all populations according to their cultures as well as social determinants of health (SDOH). In fact, doing so will certainly be a key component of promoting COVID-19 vaccines to all patient populations, once they are finally ready for the market. To show how this would be possible, we demonstrate how data extraction and AI analysis was used to uncover key insights about how parents across various cultures feel about the importance of vaccinating their kids.
Market
Vaccines represent one of the most important medical interventions in human history. Life expectancy and quality of life have been enhanced thanks to multiple vaccination programs. High vaccination rates of the routinely recommended immunizations for infant and childhood diseases have resulted in dramatic declines of polio, measles, mumps, rubella, influenza, hepatitis B, and varicella, among other conditions, and today a vast majority of diseases preventable by vaccination are reflecting historically low incidence levels. Thanks to new technologies, vaccines now have the potential to prevent not only communicable diseases in all ages, but also non-communicable diseases such as cancer and neurodegenerative disorders.1,2
Problem
The primary factors behind sub-optimal vaccination levels in America are financial challenges, access limitations, and missed opportunities for vaccines while at the HCP office. In addition, despite all scientific evidence, a remaining portion of the population either rejects vaccines due to religious or other non-evidence-based beliefs, or is not adopting the correct vaccination regimens as recommended by authorities. Most parents—even those whose children receive all recommended vaccines—have questions, concerns, or misperceptions about them.
Health literacy is considered by public health specialists as one of the best predictors of vaccine adoption. Parents, caregivers, and community members must continue to be educated, informed, and empowered to adhere to the recommended guidelines.3
Culture, language, and media play a key role in communicating healthcare-related topics. Most TV vaccine-related content is disseminated via news and entertainment programs, with limited impact in parents’ demand for vaccination, while the internet and social media have made it easier to find and disseminate concerns and misperceptions about immunization.4
Challenge
In an effort to educate and motivate parents to vaccinate their children, public and private health organizations are seeking better ways to support healthcare professionals and provide high-quality healthcare information tools. These questions remain:
- How can we better measure the confidence and relationship of moms toward vaccination?
- How can we contribute to better understand under-immunized communities and support the development of culturally aligned educational materials?
- Can internet-extracted information and data science contribute to a better understanding of the communities’ health literacy, perception of vaccines/vaccination, and help organizations to better engage individuals according to their cultures?
Solution
Cien+’s CulturIntel uses an advanced software platform to mine and structure data for insights and intelligence. Big data and an AI suite of tools aggregate and anonymize conversations online wherever they are occurring, examining who is talking, where users are talking, and what they are talking about. Advanced search techniques are applied using web spiders, crawlers, and site scraping. CulturIntel then extracts topical data, then tags that data with the origin and user, and creates a large unstructured “big dataset.”
After completion of the comprehensive data collection, natural language processing, text analytics, and social data mining are employed to examine previously described and undescribed patterns in the data. Finally, the CulturIntel strategy team outlines implications and recommendations based on discovered insights and visualizes the data in a comprehensive way.
Using this process, a company can discover insights from millions of authentic and unbiased digital discussions that mothers share every minute about their relationships, mindset, and sentiment towards vaccines.
Results
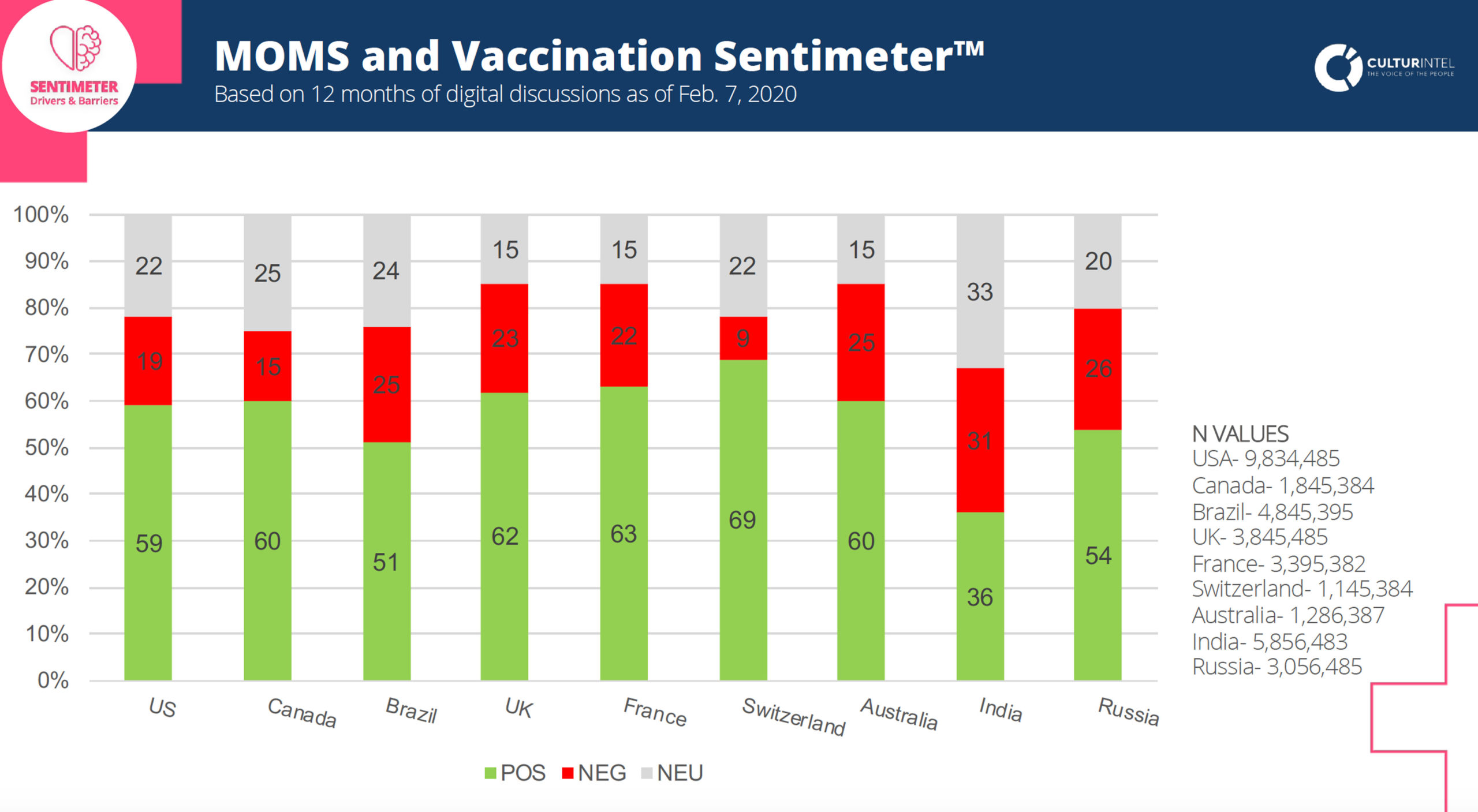
We analyzed data from contextual digital discussions about vaccination, during a 12-month period by country. More than 30 million digital discussions were identified including ~9.8M conversations in the U.S., ~5.8M in India, and ~4.8M in Brazil, among other countries.
A sentiment analysis reflected important differences in vaccine perceptions, with Russia (26%), Australia (25%), and the U.K. (23%) leading in negative perceptions; while Switzerland (69%), France (63%), and the U.K. (60%) led in positive perceptions (see Figure 1). In the U.S., 19% of the identified posts reflected negative sentiments and ~59% a positive perception.
 A deeper dive into the U.S. data identified the main factors leading the sentiments. The benefits of potential disease prevention (31%), need to protect children (29%), and the need to prevent future losses (15%) represented the most common concepts among those favoring vaccines, while safety concerns associated with autism (31%), low trust of efficacy and reliability (29%), and concerns related to the number of recommended vaccines (18%) predominated the negative sentiments.
A deeper dive into the U.S. data identified the main factors leading the sentiments. The benefits of potential disease prevention (31%), need to protect children (29%), and the need to prevent future losses (15%) represented the most common concepts among those favoring vaccines, while safety concerns associated with autism (31%), low trust of efficacy and reliability (29%), and concerns related to the number of recommended vaccines (18%) predominated the negative sentiments.
The use of this agile and tech-enabled methodology can help us further understand drivers, barriers, and decision journeys across target segments, while also keeping a pulse on the sentiment and confidence levels of people and vaccines at the community, state, and country levels. Additionally, extracted data at state and zip code levels can then be integrated with demographics, socio-economics, and SDOH-related information, so that specific health literacy levels and education needs are identified and addressed in the most culturally effective way.
In today’s fast-changing and highly diverse world, data and marketing, as much as the science behind a treatment, requires personalization that is informed and inspired by the “person” it seeks to impact—and that will require reimagining how we mine insights at scale and use agile cultural intelligence.
References:
1. Kennedy, A. (2011). “Confidence About Vaccines in the United States: Understanding Parent’s Perceptions.” Health Affairs.
2. Rappuoli, R. (2014). “Vaccines, New Opportunities for a New Society.” PNAS.
3. Robert, D. (2014). “Improving Immunization Rates of Underserved Children: A Historical Study of 10 Health Departments.” International Policy of Health Policy and Management.
4. Eysenbach, G. (2019). “A Call for a Public Health Agenda for Social Media Research.” J Med Internet Res. https://www.jmir.org/2019/12/e16661.