Trend Setting: Google and J&J Collaborate on Robotic Surgery
A robotic-assisted surgical program is currently in development by Google Inc. in collaboration with Johnson & Johnson. Ethicon, a medical device company in the Johnson & Johnson family, will work with Google to advance surgical robotics to benefit surgeons, patients and healthcare systems.
Robotic-assisted surgery is a type of minimally invasive surgery that uses technology to give surgeons greater control, access and accuracy during the surgical procedure. This minimizes trauma and scarring, which enables accelerated post-surgical healing. Google and J&J will focus on exploring methods to enhance the advanced imaging and sensors of surgical tools.
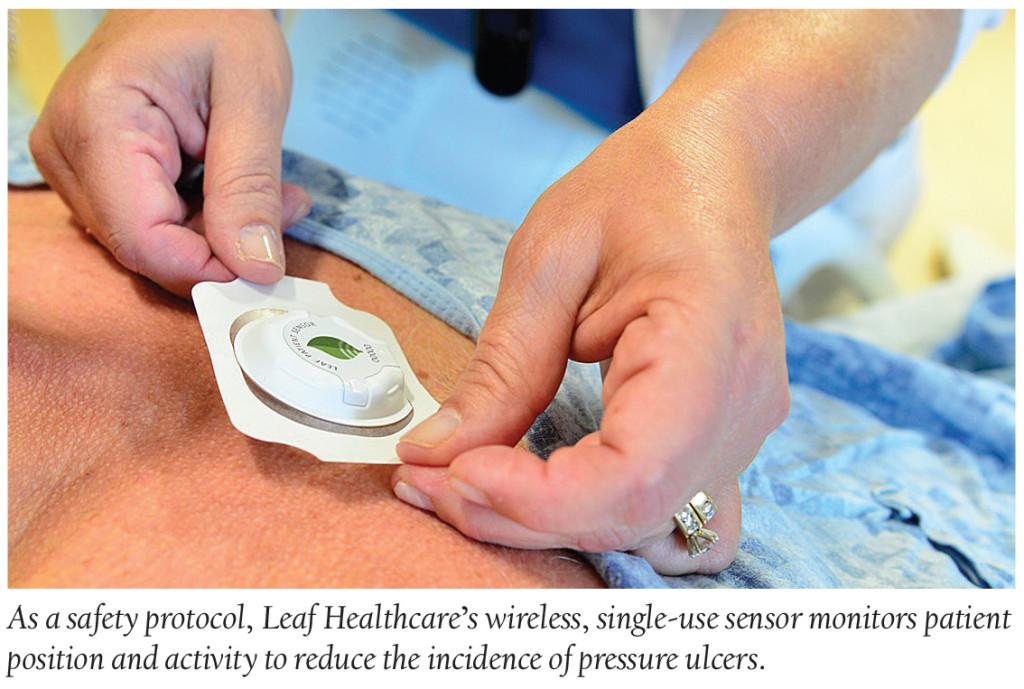
Med Device: Wearable Prevents Pressure Ulcers
A small, lightweight wearable, the Leaf Patient Monitoring system, will soon become “a safety protocol” at the Desert Valley Medical Center (DVMC) in Pleasanton, CA, the second hospital system in the U.S. to employ the device. The Leaf system is designed to prevent hospital-acquired pressure ulcers using sensors that electronically monitor a patient’s position and movements. The data acquired is wirelessly sent to monitoring stations or mobile devices—alerting caregivers to the need for patient re-positioning. Clinical studies reveal that the new sensor helps with hospital turn protocols compliance, which is essential to preventing painful pressure ulcers.
Discoveries/Innovations: Test Detects Infection Cause—In Minutes
Doctors needing to determine if an infection is viral or bacterial-based will soon be able to detect that quickly with a new point of care (PoC) test, ImmunoPoC, currently in development at MeMed, an Israel-based biotech company. According to the company, the new test measures the immune response to diagnose the source of infection within minutes—rather than the standard of several days. ImmunoPoC works by studying the proteins produced in response to a pathogen, as different proteins are released by the immune system to fight various infections.
Physicians will not only have the ability to make rapid diagnoses, but also better-informed decisions regarding antibiotic treatment at the PoC. According to the CDC, nearly half of all antibiotics prescribed are not needed, but the test can help reduce antibiotic misuse. In a 1,000-patient trial held in Israel, ImmunoPoC had a specificity and sensitivity greater than 90% in identifying whether a pathogen was a bacteria or a virus.
Therapeutic Talk: 23andMe Gears Up for New Drug Development
The Google-backed genetic testing company, 23andMe, is gearing up to use its database of customer DNA information to create new drugs—its own. The company, which licenses the raw data from its large database to researchers in government, academic and other institutions, recently hired Richard Scheller, formerly of Genentech, as its chief scientist.
In his role at 23andMe, Scheller is charged with leading the company’s new drug research and development efforts. By targeting research efforts towards patients with specific genetic markers, Scheller believes that the drug industry could potentially experience fewer drug failures—and cut the costs of new drug development. Considering that the cost of new drug discovery—and then bringing that product to market—hovers above $1 billion, 23andMe’s new venture could pave the way for a revolution in pharmaceutical R&D.