Medical Device: Ortho Clinical Diagnostics Revolutionizes Lab Tech
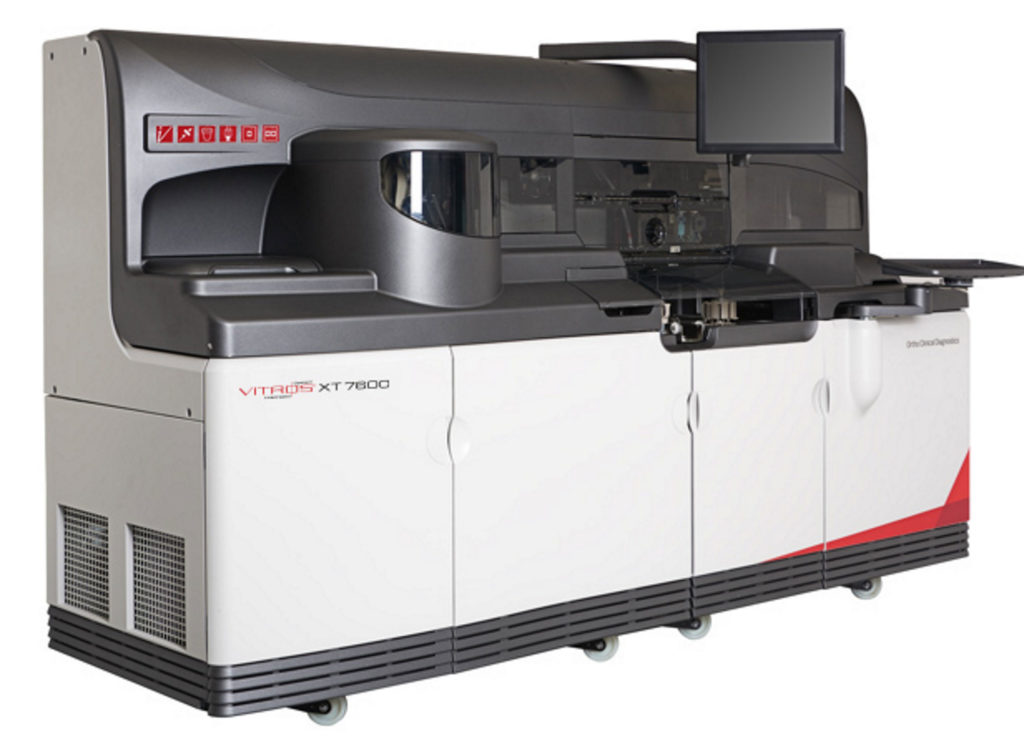

The FDA has approved VITROS XT 7600 Integrated System, allowing Ortho Clinical Diagnostics to bring innovative DIGITAL CHEMISTRY technology to clinical lab management in the U.S. The system, available for purchase at the start of the year, combines Ortho’s proprietary MicroSlide technology, which is a full testing environment on a postage-stamp-sized piece of film that enables precise and accurate testing, with sophisticated digital imaging capabilities as well as the potential to perform two separate lab tests simultaneously, for the first time. The system also utilizes Ortho’s dry slide technology. Unlike traditional wet chemistry systems, which require highly purified water and complex plumbing systems to operate, this tech does not require water to run, eliminating the risk that poor water quality could impact test results and making testing possible in limited resource environments.
“It’s an exciting time for clinical labs, and today’s clearance of Ortho’s VITROS XT 7600 System represents a fundamental improvement in the way labs can operate, now and in the future,” said Jennifer Paine, Ortho’s Chief Product Portfolio Officer in a statement. “VITROS XT 7600, along with DIGITAL CHEMISTRY, harnesses the power of our proprietary dry slide technology to deliver high-quality test results and higher throughput—all within the lab’s existing physical footprint.”
The system’s multi-test processing saves time and space in the lab, and increases productivity, with less patient sample required for testing, an important advantage for vulnerable patients or those with venous access issues. This is all done while saving time and space in the lab, potentially cutting overall costs for test processing.
Discoveries/Innovations: New Electronic Bandages Improve Wound Healing
A little electronic shock does a body good. Engineers at the University of Wisconsin-Madison developed a new, low-cost dressing that leverages energy generated from a patient’s own motions to apply gentle electrical pulses to the wound. This method was able to reduce healing time from nearly two weeks to just three days when tested on rodents.
The dressings consist of small electrodes that are linked to a band holding energy-harvesting units called nanogenerators, which are looped around a wearer’s torso. A patient’s natural breathing, which causes the expansion and contraction of the ribcage, is enough to power the nanogenerators and deliver the low-intensity electric pulses.
The researchers next step is to test the bandage on pig skin, which closely mimics human tissue.
TeleMed Texts: Digital Therapeutic for Opioid Abuse Cleared
The FDA has approved the first prescription digital therapeutic for patients being treated for opioid abuse or dependency. Pear Therapeutics’ soon-to-be-launched reSET-O smartphone app is intended to be used with standard-treatment medication, especially transmucosal buprenorphine film, by keeping users adherent for their first 12 weeks.
The app assists patients in this vulnerable time by providing interactive therapy lessons that challenge harmful behaviors, help develop coping strategies, and reinforce the importance of taking medication. reSET-O also supports communication between visits, allowing patients to self-report cravings and triggers to their physician, and their buprenorphine use. “Medical devices, including digital health devices like mobile medical apps, have the potential to play a unique and important role in contributing to these treatment efforts,” FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb, MD said in a statement regarding opioid substance abuse. “We know medication-assisted treatment works and we support novel ways to keep individuals more engaged in their treatment programs and to provide clinicians with new ways to intervene to help them remain in treatment.” reSET-O saw significant improvements in retention in the 170 patients randomized to either the standard buprenorphine treatment or its combination with the app in a clinical trial sponsored by the NIH’s National Institute on Drug Abuse.
Study Sessions: Link Discovered Between Gut MicroBiome and Diabetes Drugs
 In an attempt to answer why diabetes drugs work for some patents and not others, researchers at the Wake Forest School of Medicine started to examine our gut bacteria. What they found were major differences in how well various diabetes drugs worked depending on whether they were administered via IV or orally, passing through the gut.
In an attempt to answer why diabetes drugs work for some patents and not others, researchers at the Wake Forest School of Medicine started to examine our gut bacteria. What they found were major differences in how well various diabetes drugs worked depending on whether they were administered via IV or orally, passing through the gut.
Type 2 diabetes, which has increased substantially globally, means patients have an inability to properly metabolize carbs and fats. In turn, one main function of gut microbiota is to metabolize non-digestive carbohydrates and regulate a person’s metabolism. “Our review showed that the metabolic capacity of a patient’s microbiome could influence the absorption and function of these drugs by making them pharmacologically active, inactive, or even toxic,” said Hariom Yadav, PhD, Assistant Professor of Molecular Medicine at the School of Medicine, Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center. “We believe that differences in an individual’s microbiome help explain why drugs will show a 90% or 50% optimum efficacy, but never 100%.”
Unfortunately, our knowledge of the gut biome only goes back about a decade, and there currently aren’t ways to modify it. If research makes this possible, it can serve as an effective way to modulate the effectiveness of type 2 diabetes medications and perhaps therapies for an even wider range of diseases.
Trend Setting: First Baby Born After Uterus Transplant
For the first time, a baby was successfully birthed by a mother who received a uterus transplant from a deceased donor. While very few babies have been born to women who have received a uterine transplant from living relatives, this is the first birth that establishes the possibility that this can be done more sustainably, through deceased donors. The baby was safely born in the Hospital das Clínicas at the University of São Paulo School of Medicine in Brazil, where Dr. Dani Ejzenberg, an OB/GYN at the University of Sao Paulo Hospital, and Dr. Wellington Andraus, a transplant surgeon at the Sao Paulo University School of Medicine, wrote that “The results provide proof-of-concept for a new treatment option for absolute uterine factor infertility.”
The new mother was born without a uterus due to a rare genetic condition called Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser syndrome. Months before receiving the transplant, the woman received in vitro fertilization, providing her with eggs. The short time table was opted for to reduce risk of infection. Her donor was chosen because she was relatively young, 45, and had three vaginal deliveries during her life, she had no reported sexual disease, and a matched blood type. After five months, the woman experienced her first menstruation and 10 days later, became pregnant.
Without any issues during pregnancy, the baby girl was born via C-section when the transplanted uterus was also removed so the mother could cease immunosuppressant therapy. Now, the baby is over seven months old and perfectly healthy, setting a hopeful precedent for uterus transplantation.
Therapeutic Talk: Axolotl Releases Stem Cell Injection

Axolotl Biologix, a biotech company focused on regeneration by developing and manufacturing regenerative human cell and tissue medical technologies, has launched a new product for wound care. The Axolotl Shot is a regenerative fluid derived from the amniotic components of the placenta to promote regeneration and repair of damaged or degenerated tissues. The ambient temperature regenerative fluid preloaded into a syringe for ease of use by physicians. Axolotl uses its proprietary BioSym process to yield growth factors and cytokines known to stimulate cellular growth and repair.
“Our new Axolotl Biologix treatment option uses the latest advances in biotechnology to improve patient outcomes while making it more convenient for physicians,” Robert Kellar, PhD, Chief Science Officer, said in a statement. “The Axolotl Shot is preloaded in 1 mL and 2 mL volumes, terminally irradiated for use in surgical applications, and since it can be stored at room temperature there are no storage concerns or down time waiting for product to thaw.”
FDA Update
Drug Approvals
The FDA granted Celltrion approval of biosimilar, Herzuma (trastuzumab-pkrb) for the treatment of patients with HER2-positive breast cancer. Herzuma is a biosimilar to Genentech’s Herceptin (trastuzumab).
Catalyst Pharmaceuticals received FDA approval of Firdapse (amifampridine), the first drug to treat Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) in adults. LEMS is a rare autoimmune disorder that affects the connection between nerves and muscles and causes weakness and other symptoms in affected patients, especially those with cancer.
Maybe Pharma announced the approval of a New Drug Application for Tolsura, indicated for the treatment of certain systemic fungal infections in adult patients. These types of infections most commonly occur in vulnerable or immunocompromised patients, for example, those with a history of cancer, transplants (solid organ or bone marrow), HIV/AIDS, or chronic rheumatic disorders, and are often associated with high mortality rates or long-term health issues.
The FDA expanded the indication for Amgen’s Nplate (romiplostim) to include its use in pediatric patients aged one year and older with immune thrombocytopenia for at least six months and who experienced an insufficient response to corticosteroids, immunoglobulins, or splenectomy.
Loxo Oncology’s Vitrakvi (larotrectinib), a treatment for adult and pediatric patients whose cancers have a specific genetic feature (biomarker), was granted accelerated approval, breakthrough therapy, and Orphan Drug designation by the FDA. The approval marks a new paradigm in the development of gene-focused cancer drugs that are “tissue agnostic,” rather than treating them at their origin site.
Med Device Update
Spinal Elements received FDA approval of claims related to the macro-, micro-, and nano-surface structure of its Ti-Bond surface coating technology. The titanium-based coating covers many of the company’s interbody devices that surgeons use for vertebral fusion, providing the latest, proven technology without compromising imaging characteristics, spinal loading conditions, or long-term performance.