Brand Beat: FDA Approves Breakthrough Beauty Product
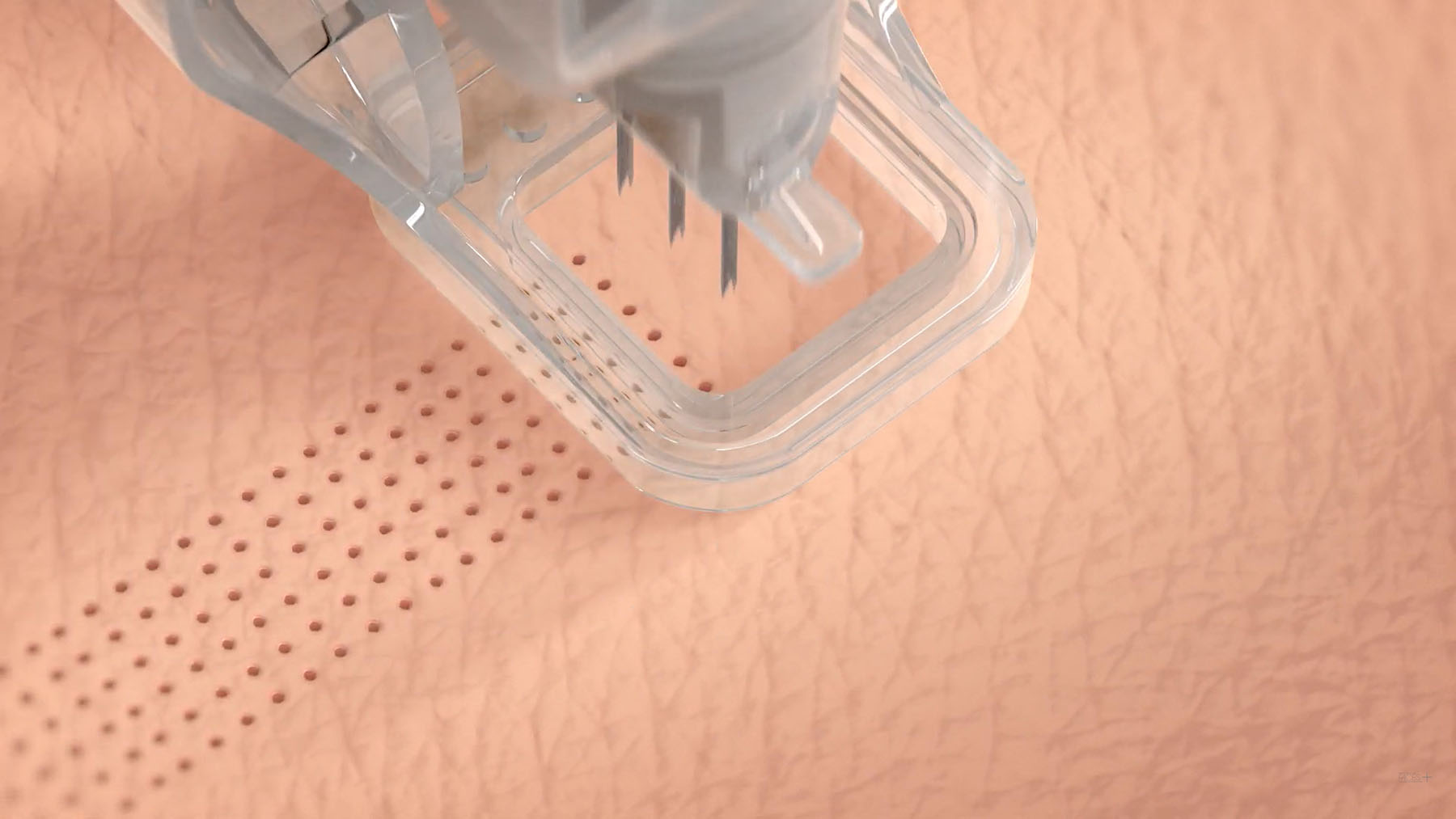
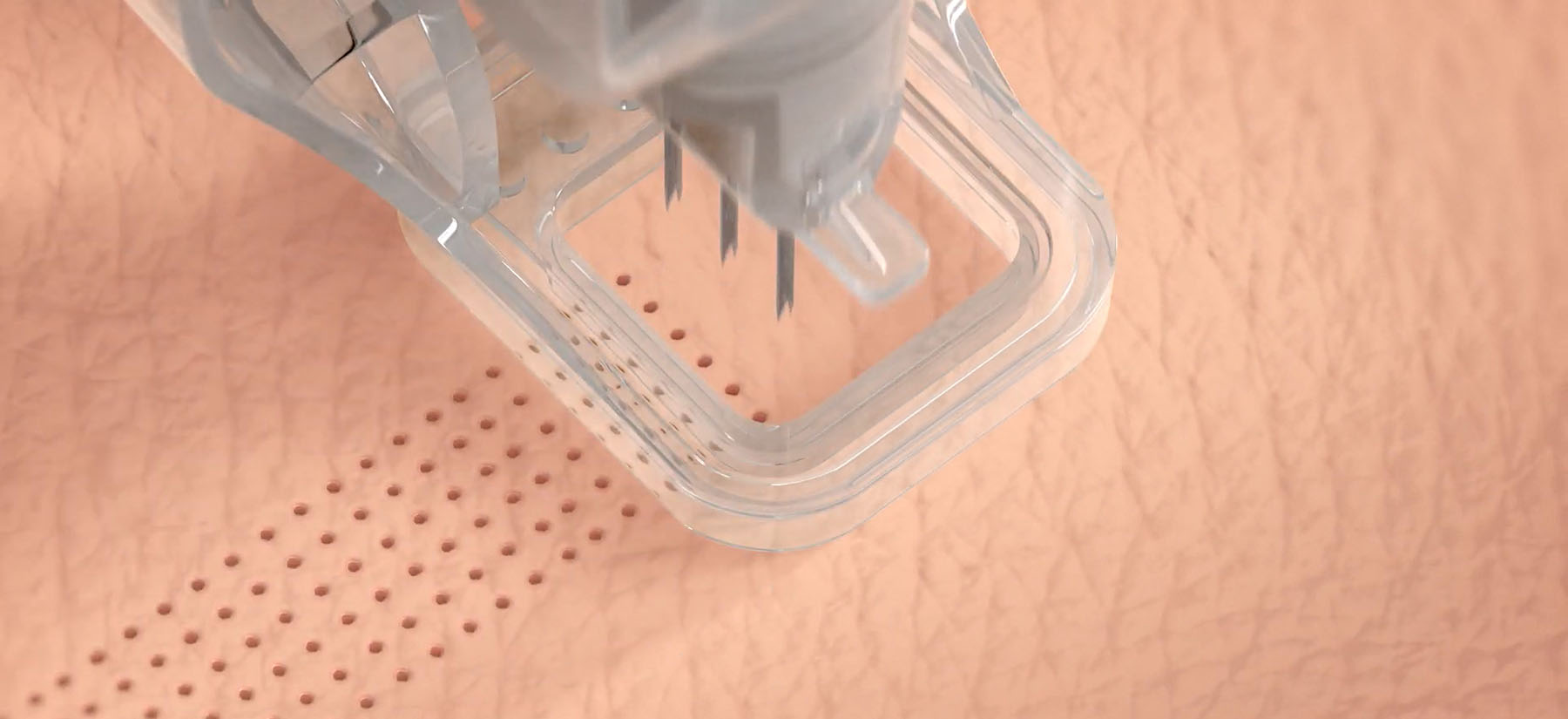
Cytrellis, a medical device company developing aesthetic products, received the FDA go-ahead for their proprietary Micro-Coring technology for treating wrinkles of certain areas of the face. The minimally invasive Ellacor system removes micro-sized portions of excess skin with no evident scarring, unlike surgical procedures. It also requires less healing time than traditional laser-based ablations for aging skin.
Ellacor works with micro-hollow needles to remove full thickness micro cores of dermal and epidermal tissues while the patient is under local anesthesia. The process removes 5% to 10% of excess skin, which reduces appearance of wrinkles and sagging in the middle and lower face, but since the procedure leaves no scarring it can be done multiple times, increasing the percent of excess skin removal. The hollow needle holes are extremely small, taking with it cores of skin small enough not to scar or disturb the skin, requiring about three days for full facial healing. Ellacor is intended to be done multiple times over years to help maintain facial skin’s youthful appearance.
Discoveries & Innovations: Can Allergy Meds Help Cancer Treatment?
Researchers from University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center made a surprising discovery when analyzing how common medications might boost the immune system’s ability to fight cancer cells. The team studied patients with melanoma or lung cancer and found that those who were taking antihistamines and checkpoint inhibitors at the same time had significantly better outcomes than those of patients who did not take allergy drugs.
The antihistamines were specifically targeting histamine receptor H1 (HRH1). When analyzing HRH1, they found that high levels of the histamine receptor in tumors are related to malfunctioning T cells, which are the immune cells that are vital to launching an effective immune response to cancer. With allergy medications binding these receptors, immune cells are better able to respond to checkpoint inhibiting drugs to fight tumor cells. The researchers believe using antihistamines in cancer patients who have high levels of histamines in their blood could be useful for enhancing immunotherapies and are now designing clinical trials to test combination treatments for different cancers.
Trendsetting: New VR Surgery Prep Cleared

The FDA has cleared a new technology from PrecisionOS that will allow surgeons to examine a patient’s individual anatomy through virtual reality to prepare for surgery. InVisionOS, which will be available for U.S. surgeons in 2022, will use a hospital’s existing CT scans to reconstruct a virtual, 3D model in seconds. Using an Oculus Quest 2 VR headset, a surgeon can zoom in and manipulate the patient’s specific anatomical structure to better plan for each surgery. It is the first technology to allow surgeons to explore every aspect of the patient anatomy captured by CT scan.
The InVisionOS will also be used to improve surgical training procedures. Trainees using the VR can walk around and make decisions with highly realistic anatomical models. The system is especially powerful for orthopedic surgeries, opening opportunities for medical device companies to provide faster and more cost-effective training options for their clients and sales teams.
Therapeutic Talk: New Malaria Vaccine Is Groundbreaking Despite Drawbacks
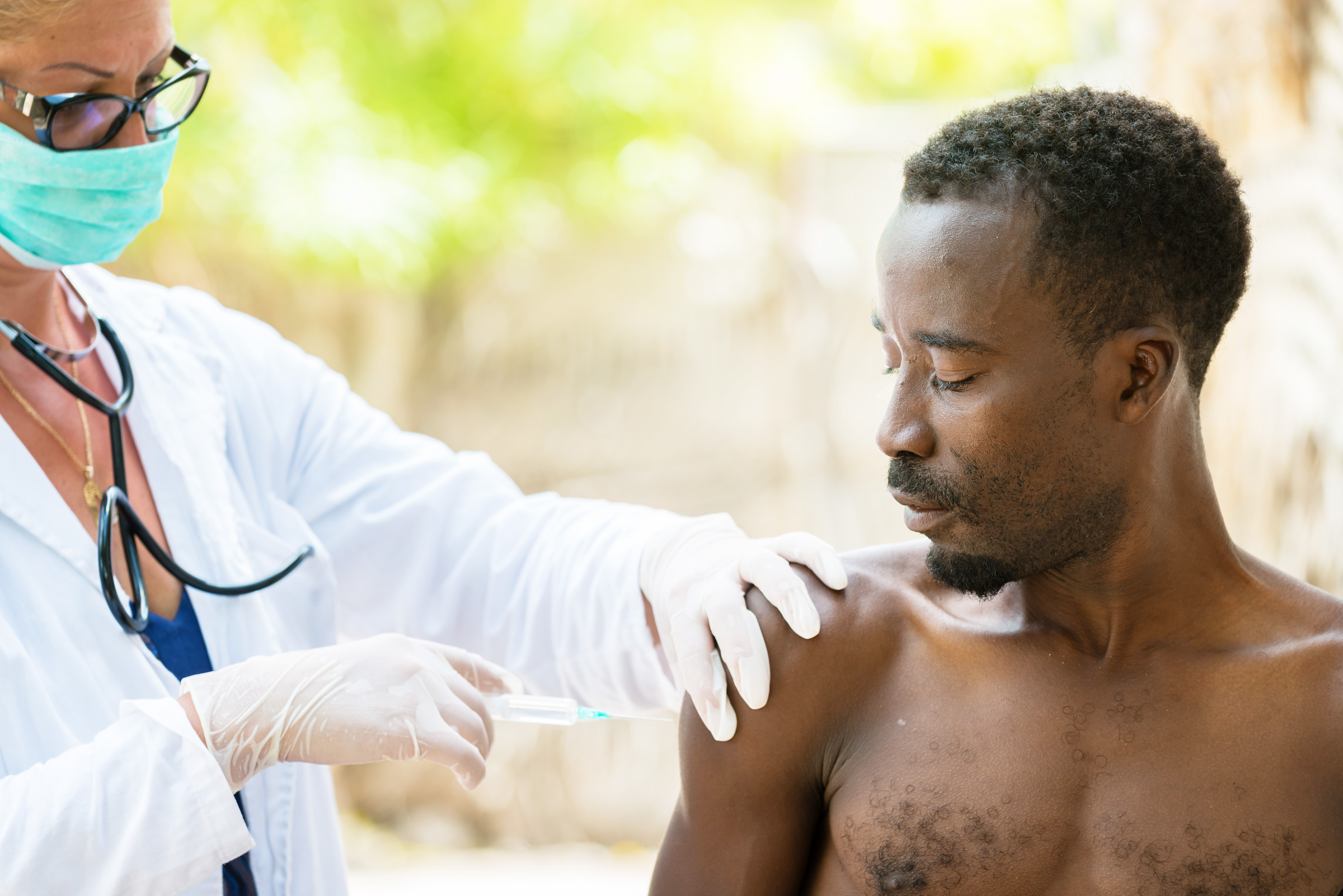
This year marked the historic approval of the first-ever vaccine against P. falciparum malaria transmission, known as RTS,S. The vaccine, developed by GlaxoSmithKline, is also the first developed for any parasitic disease transmission. RTS,S is the result of an ongoing pilot program from 2019 run in Ghana, Malawi, and Kenya, where P. falciparum malaria is the deadliest; more than 260,000 African children under the age of five die from malaria annually.
The program has administered 2.3 million vaccine doses to date, reaching more than 800,000 children. Despite widespread distribution and its successful integration with other malaria intervention methods, RTS,S was only found to be 30% effective against deadly malaria cases and 40% effective in mitigating standard malaria cases.
WHO recently made official recommendations for widespread use of RTS,S among children in sub-Saharan Africa and in other regions with moderate to high P. falciparum malaria transmission.
“For centuries, malaria has stalked sub-Saharan Africa, causing immense personal suffering,” said Dr. Matshidiso Moeti, WHO Regional Director for Africa, in a public statement. “We have long hoped for an effective malaria vaccine and now for the first time ever, we have such a vaccine recommended for widespread use. [This] recommendation offers a glimmer of hope for the continent which shoulders the heaviest burden of the disease and we expect many more African children to be protected from malaria and grow into healthy adults.”
Now, researchers and HCPs alike are expressing concern about the low-efficacy vaccine diverting funds from other control methods, such as insecticide programs and functional health systems, that are needed more than ever as malaria incidences continue to rise with global temperatures year over year. In addition, GSK stated it will make 15 million doses of the vaccine available annually for just over the cost of production. However, 100 million doses will be needed annually if all children in high-burden countries are to receive the shot.
While 30% efficacy will not be suitable for long-term community protection and trust, WHO stands by its recommendation to use the vaccine along with other malaria prevention methods in order to potentially save tens of thousands of lives each year.
FDA Update
Drug Approvals
Aadi Bioscience, Inc. received FDA approval for Fyarro, a new drug designed for adult patients with locally advanced unresectable or metastatic malignant perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa). The sirolimus protein-bound particles are administered via injectable suspension. PEComas are rare tumors that form in soft tissues of the stomach, intestines, lungs, female reproductive organs, and genitourinary organs.
The FDA approved a new injectable treatment for adults with polycythemia vera, a rare blood disease that causes the body to overproduce red blood cells. About 6,200 Americans suffer from polycythemia, which thickens the blood and increases risk of clotting. PharmaEssentia Corporation’s BESREMi is the first medication to be approved for the rare disease. BESREMi reduces the amount of red blood cells in the body and is used in combination with phlebotomies, or procedures that remove excess blood cells through a needle in a vein.
Cytalux (pafolacianine) received FDA approval as an imaging drug intended to assist surgeons in identifying ovarian cancer lesions. On Target Laboratories designed the intravenous injection as a diagnostic agent to be administered prior to surgery that will help surgeons locate additional ovarian cancerous tissues that are usually difficult to detect during surgery. Cytalux binds to a specific protein receptor that is overproduced in cancerous ovarian tissue and then illuminates under fluorescent light. About 13,000 women have died of ovarian cancer in the U.S. and the conventional treatment is to surgically remove as many tumors as possible.
Med Device Approvals
Hyperfine’s portable magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) device Swoop received new FDA clearance that adds advanced image reconstruction technology using deep learning to the device’s capabilities. This process can improve image quality by 60%, according to FierceBiotech, which elevates the diagnostic value of the device by producing less blurry images.
The FDA approved AppliedVR’s EaseVRx, a prescription-use immersive VR system that uses cognitive behavioral therapy and other behavioral methods to help with pain reduction in patients 18 years of age and older with diagnosed chronic lower back pain. The treatment program consists of 56 VR sessions that are 2-16 minutes long, which are given over the course of eight weeks.