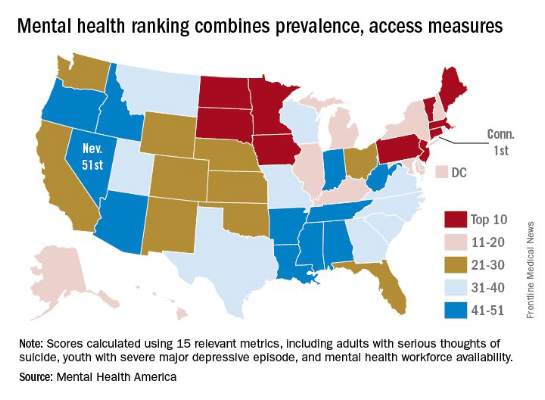
The state of mental health in Connecticut makes it the state for mental health in 2016, according to the advocacy group Mental Health America.
Connecticut had the top overall score in an analysis that combined 15 prevalence and access measures for adults and children. Massachusetts finished second, and Vermont was third for a New England sweep of the medal positions, with South Dakota and Minnesota rounding out the top five, Mental Health America reported.
When there are winners, of course, there also must be losers, and in this case the bottom five states for mental health are Nevada (51st), Arizona (50th), Oregon (49th), Idaho (48th), and Arkansas (46th), the analysis showed.
Connecticut finished first in the subgroups of measures pertaining to adults and to prevalence, Minnesota ranked first in the subgroup of child measures, and Vermont was first in access to care. Nevada was 51st in the adult measures and in access to care, Arkansas ranked 51st in the child measures, and Oregon was 51st in the prevalence ranking, noted Mental Health America, which also gave a ranking to the District of Columbia.
Considerable variation can be seen between states on some of the 15 measures. For mental health workforce availability, Massachusetts was first with 1 mental health provider per 200 residents, while Alabama was 51st with one provider for every 1,200 individuals. In South Dakota, 39.5% of children with severe depression received some consistent treatment, compared with 9.4% in Nevada. In Hawaii, 13.6% of adults with mental illness were not able to get the treatment they needed, compared with 25.9% in Missouri, according to Mental Health America.
The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration was the main source of data for the analysis; other sources included the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, and the Department of Education.